鐵調素Hepcidin-25作為鐵代謝和免疫反應關鍵調節因子的功能和作用
在生命科學的探索中,Hepcidin-25(鐵調素,M28234,AbMole)作為鐵代謝和免疫反應的關鍵調節因子,一直是研究的熱點。它不僅在基礎生物學中扮演著重要角色,還為理解生物體內的復雜機制提供了新的視角。AbMole 作為您可靠的科研伙伴,致力于提供高品質的 Hepcidin-25試劑產品,助力前沿探索。AbMole為全球科研客戶提供高純度、高生物活性的抑制劑、細胞因子、人源單抗、天然產物、熒光染料、多肽、靶點蛋白、化合物庫、抗生素等試劑,全球大量文獻專利引用。
1、Hepcidin-25(M28234,AbMole):鐵代謝的關鍵調節者
Hepcidin-25的核心功能是調節鐵的吸收和分布。通過與細胞表面的鐵轉運蛋白 Ferroportin 結合,Hepcidin-25 能夠精準地控制鐵的輸出,從而維持體內鐵的平衡。這種調節機制在生物體的正常生理過程中至關重要,例如在腸道鐵吸收、肝臟鐵儲存以及紅細胞生成等過程中發揮著不可或缺的作用。Hepcidin-25(M28234)是研究慢性疾病貧血(ACD)、缺鐵性貧血、地中海貧血、鐵過載相關疾病等動物模型的重要試劑。2014年,AbMole的兩款抑制劑分別被西班牙國家心血管研究中心和美國哥倫比亞大學用于動物體內實驗,相關科研成果發表于頂刊 Nature 和 Nature Medicine。
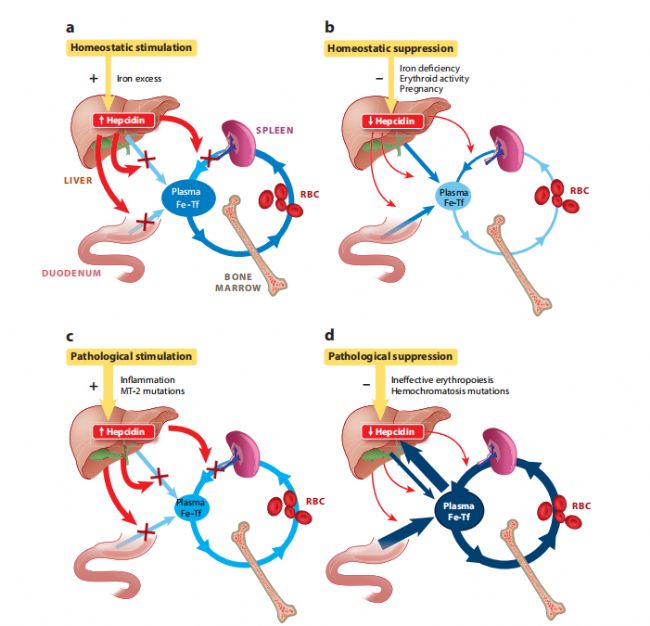
圖1 Hepcidin-25的生理功能
2、 Hepcidin-25(M28234,AbMole):免疫反應的效應調節因子
Hepcidin-25(M28234)在宿主防御中具有重要作用。在感染或炎癥狀態下,Hepcidin-25 的水平升高,導致血清鐵水平下降,這種機制被稱為“缺鐵性貧血”。這種鐵的限制策略可以抑制病原體的生長,從而增強宿主的防御能力[2]。在單核巨噬細胞中,Hepcidin-25(鐵調素,M28234)通過抑制 FPN1,阻斷巨噬細胞對衰老紅細胞鐵的再循環利用。炎癥狀態下,Hepcidin-25 表達升高導致巨噬細胞鐵隔離,形成不利于病原體生長的低鐵環境,這種 "營養免疫" 機制在宿主防御中發揮重要作用[3]。而在一些自身免疫疾病的研究中,常常伴隨著炎癥因子的異常表達,這些炎癥因子如IL-6會誘導Hepcidin-25 的表達,進而導致鐵代謝紊亂,因此Hepcidin-25(鐵調素,M28234)也是自身免疫疾病中的一個重要標志物和重要的研究靶點。
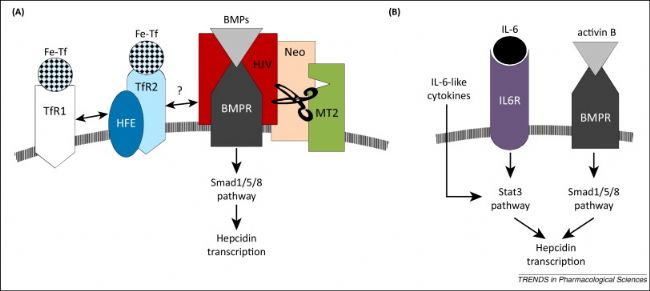
圖2. 炎癥因子與Hepcidin - 25的轉錄調節
3、 Hepcidin-25:廣泛的抗菌活性
Hepcidin-25(M28234,AbMole) 對革蘭氏陽性菌、革蘭氏陰性菌及真菌均有抑制活性。其抗菌機制包括:1)通過靜電作用吸附于微生物細胞膜,破壞膜完整性導致離子泄漏;2)螯合細胞外鐵離子,干擾病原體鐵獲取;3)抑制細菌生物被膜形成,降低群體感應信號傳導效率。研究表明,其對金黃色葡萄球菌最小抑菌濃度(MIC)可達 1-4 μM。AbMole是ChemBridge中國區官方指定合作伙伴。
參考文獻
[1] NEMETH E, GANZ T. Hepcidin and Iron in Health and Disease [J]. Annual review of medicine, 2023, 74: 261-77.
[2] KALI A, CHARLES M V, SEETHARAM R S. Hepcidin - A novel biomarker with changing trends [J]. Pharmacognosy reviews, 2015, 9(17): 35-40.
[3] SCHMIDT P J. Regulation of Iron Metabolism by Hepcidin under Conditions of Inflammation [J]. The Journal of biological chemistry, 2015, 290(31): 18975-83.
[4] RUCHALA P, NEMETH E. The pathophysiology and pharmacology of hepcidin [J]. Trends in pharmacological sciences, 2014, 35(3): 155-61.
Copyright(C) 1998-2025 生物器材網 電話:021-64166852;13621656896 E-mail:info@bio-equip.com





